HVDC technology facilitates the transmission of large amounts of power over long distances using direct current. There are two primary HVDC technologies: line-commutated converters (LCC) based on thyristors, and self-commutated voltage source converters (VSC) based on IGBTs.
- LCC-based HVDC systems consume reactive power and require large AC filters, necessitating connection to a strong power grid. They are primarily used for high-power transmission over long distances.
- MMC-based VSC-HVDC systems produce very low harmonic distortion, so only modest high-frequency AC filters are needed. They can continuously generate or absorb reactive power, interconnect asynchronous grids, and maintain voltage even on very weak or “dead” networks. These attributes make them the technology of choice for integrating renewable generation—especially offshore wind farms—and for building multi-terminal or meshed HVDC networks.
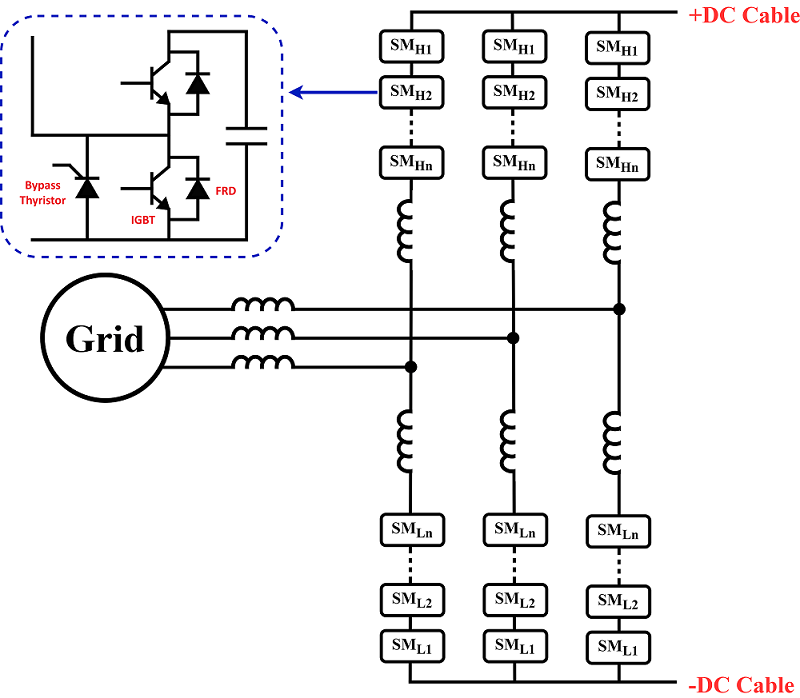
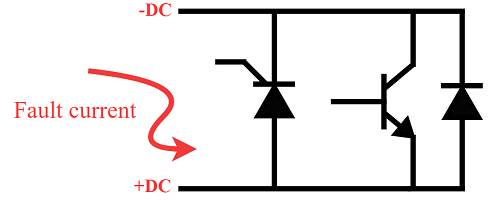
In MMC VSC HVDC systems, bypass thyristors are employed to protect the IGBT modules by diverting fault current away from the freewheeling diodes (FRDs) in the event of a DC-side fault. This reduces the electrical and thermal stress on the FRDs and enhances the fault-handling capability of the half-bridge submodules.
Dynex Reverse Asymmetric Bypass Thyristor
In MMC HVDC systems, at voltage ratings of 6.5kV, standard thyristor designs use relatively thick silicon, leading to high on state dynamic forward voltage, thus limiting their protection capability in this application.
Dynex has released a 6.5kV reverse asymmetric bypass thyristor (RAByT), designed with an N-buffer diffusion located on the cathode side of the device enabling significantly thinner silicon. Furthermore, an optimised interdigitated gate-arm structure gives low anode voltage latching, providing further enhanced protection. Finally, the high-resistivity N-base design improves the device’s reliability (cosmic ray FIT rating), making the RAByT a more robust protection solution.
Key Features
- Lower on-state voltage (VTm)
- Increased surge current capability
- Triggering with a lower anode-side voltage (low pick-up voltage)
- Suitable DC leakage current
- Reduced cosmic ray FIT rating
In summary, Dynex reverse asymmetric bypass thyristors contribute significantly to HVDC systems reliability by swiftly handling fault currents and ensuring continuous power transmission. This capability is especially critical today, as renewable energy sources increasingly dominate power generation, resulting in reduced grid inertia compared to traditional fossil fuel power stations.
Should you require any adjustments to meet the specific requirements for your applications, please contact us. We are equipped to design and develop customised products tailored to your needs.